How the Redirector works
Figure 1 illustrates how the Redirector sends
the client data to the Telnet server and sends to the client the responding
data from the Telnet server.
Figure 1. How the Redirector
works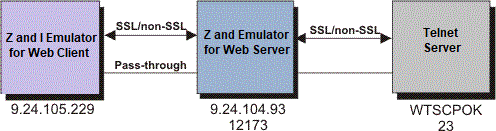

The Redirector can be configured in any one of the following four
modes:
- Passthrough
- The Redirector communicates with the Telnet server and the client without changing the content of the data.
- Client-side
 The client and the Redirector communicate in a secure
session using TLS (the content is encrypted/decrypted).
The client and the Redirector communicate in a secure
session using TLS (the content is encrypted/decrypted).
- The Redirector and the Telnet server communicate in a non-secure session.
- Host-side
- The client and the Redirector communicate in a non-secure session.
 The Redirector and the Telnet server communicate in
a secure session using TLS (the content is encrypted/decrypted)
The Redirector and the Telnet server communicate in
a secure session using TLS (the content is encrypted/decrypted)
- Both
 The client and the Redirector communicate in a secure
session using TLS (the content is encrypted/decrypted).
The client and the Redirector communicate in a secure
session using TLS (the content is encrypted/decrypted).
 The Redirector and the Telnet server communicate in
a secure session using TLS (the content is encrypted/decrypted).
The Redirector and the Telnet server communicate in
a secure session using TLS (the content is encrypted/decrypted).
 Before you use the Client-side, Server-side, or Both
modes, you need to create the ServerKeyStore.jks (if configured to use JSSE)
for the Redirector.
Before you use the Client-side, Server-side, or Both
modes, you need to create the ServerKeyStore.jks (if configured to use JSSE)
for the Redirector.
You can use the Pass-through mode when encryption by the Redirector is not necessary, either because the data stream does not need to be encrypted, or because the data stream is already encrypted between the client and the Telnet server. you need to use the Pass-through mode if the Z and I Emulator for Web client is connecting through the Redirector to a host that requires client authentication or Express Logon.
Refer to Adding a host to the Redirector in the online help for more information.